Are you an international smuggler who needs to make a hundred thousand dollar transaction without the FBI finding out? Or are you an artist trying to find a way to sell their drawings online? Both of those problems can be fixed with a little bit of blockchain, the same technology that powers Bitcoin. You might be wondering, “How can computer money help with any of those problems?” Well, blockchain has many more uses than just cryptocurrencies and will be an important part of our future.
What is Blockchain?
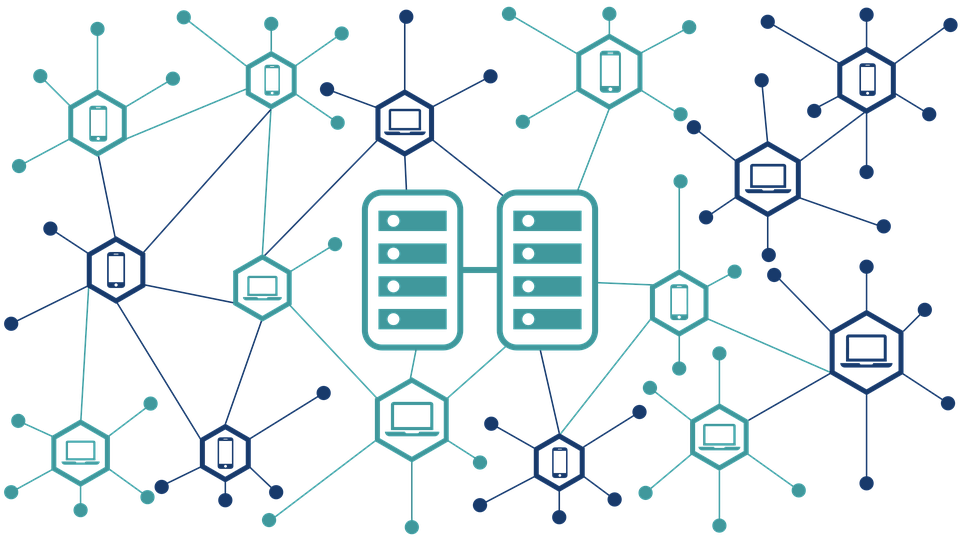
In simple terms, blockchain is a decentralized immutable distributed virtual ledger that records transactions and tracks digital assets. Alright, that wasn’t so simple. Let’s break down some of the terms:
Blockchain is a Virtual Ledger
Think of blockchain as a book, with each page being a block of data and each line being an entry on the block. When the block is verified by “miners”, it is then permanently added to the blockchain. Typically, blockchains are used in recording currency exchanges such as Bitcoin. Every bitcoin transaction is added to a block where a miner verifies that all the data is correct and the block is made permanent on the blockchain.
Blockchain is Decentralized
Where does our money come from? The answer is simple: the government. Traditional currencies are centralized, which means that the government is responsible for creating them and stabilizing their value. However, a blockchain is decentralized and controlled by its users. Users can mint their own coins using different algorithms and methods depending on the blockchain. All users have access to all the data and can add entries to the blockchain. Some users can volunteer to verify entries to make sure that the info on the blockchain is true. This puts power in the hands of the people, without having someone else take away control.
Blockchain is Immutable
On all blockchains, every record is permanent and cannot be edited or deleted. All data is encrypted using hash functions which essentially take the hash value of the previous blocks in a blockchain and use math to turn them into a unique value which becomes the hash value of the next block. This value is impossible to reverse engineer (find out the inputs with the output), so hackers can’t try to add a fake block to the blockchain. Since, all the blocks in a chain have their hashes linked together, if someone changes the data of one block, it changes the hash function of another block, making changes easily identifiable. Changing multiple blocks would require a lot of computing power which is impossible with today’s technology, so the data is safe.
The Exception
Before we continue, there is a special category of blockchains which seems to break the rules of typical blockchains. Most blockchains are public, meaning anyone can participate and use them. However, private blockchains exist and are managed by a single person/group and users need permission to access the blockchain. Sometimes there are also administrators for the blockchain who have the power to delete or modify entries. Despite these differences, private blockchains still act as a ledger where participants can add and verify data. One example of a private blockchain is Hyperledger Fabric, a blockchain project that helps businesses develop blockchain related applications. To use Hyperledger Fabric, businesses have to apply for permission, which makes this a private blockchain.
What Can We Use Blockchain For?
Since its birth in 2008, blockchain is used in almost every industry. Of course, the biggest use for blockchain is:
Cryptocurrency
With such a secure technology that is fully transparent to the users, no wonder blockchain’s very first use was for money transactions. Unlike traditional currencies, users won’t have to worry about a middleman when sending money. Normally, if you wanted to send the month’s rent to your landlord who’s overseas, you would have to make a bank transfer or use apps like PayPal that you have to place trust in. With cryptocurrencies, all the data is public and all transactions are verified by computers, so you don’t have to place trust in a shady middleman. This also means that there is no way to undo a transaction, which can be a win or a loss depending on your uses.
However, transferring money is pathetically slow, with Bitcoin having a speed of 4.6 transactions per second compared to Visa’s 1700 transactions per second since Bitcoin blocks take 10 minutes on average to mine. Additionally, many cryptocurrencies are very volatile and impractical. You could spend $1000 worth of Ether on a new computer and a year later, that same amount of Ether is worth $5000. Of course, there are constant improvements on blockchain to overcome these problems, for example Litecoin is much faster than Bitcoin due to blocks being generated much more quickly. Additionally, stablecoins are on the rise and are backed by stable assets such as gold, silver, or even fiat currencies. This makes them more stable in value and are useful for being used as currency. As the future grows near, cryptocurrencies will continue to change and evolve.
Digital Marketplace
Everyone has used Amazon in the past 2 years because of the pandemic. But while Amazon deals with selling physical objects, online stores such as TheOnly.Biz, Opensea.io allow users to buy Non-Fungible Tokens (NFT). An NFT is simply a file that lives on a blockchain. It is called non-fungible since every NFT is different from the other. In the real world, every single piece of money is the same. There isn’t a reason to prefer one dollar note over the other, but with NFTs, each one is unique. NFTs can be anything digital, such as a music file, a document, or a game. With NFTs, you can prove your ownership of an asset and it is easy to track exchanges of the asset. This makes them useful as art pieces, collectibles, website domains, or even patents!
Customer-Supplier Transparency
The process of getting raw materials and turning them into usable products in your home has many blind spots for both consumers as well as others involved in the supply chain. For example, you have no idea which factory your shirt was made in, and the manufacturer has no idea when you bought that shirt from Walmart. Every participant in the chain should be able to know what happened or will happen to the item they paid for, whether you want to be eco-friendly or want to make sure you are paying a fair price. Blockchain can fix this issue by maintaining important records such as order invoices, receipts, and bank loan records whenever a product moves from one stage of the supply chain to the This way, every participant knows the costs involved and where their product traveled when bringing it to the consumer.
Online Voting
Voting season brings a flurry of emotions to the whole nation as the new leader is decided. However, it isn’t always possible for someone to go to the voting center for a variety of reasons. With a blockchain, anyone can vote from the comfort of their couch with their phone and proof of id. As a bonus, all the numbers will be visible to the public after the election, so no one can make accusations of fraudulent counting. However, there are still challenges that need to be addressed. Complete anonymity cannot be guaranteed, especially if someone has a virus on their device, and it is impossible to be guarantee that the person making the vote is indeed themself.
Patent Records
With blockchain’s immutable nature, using it to store patents and copyright info will mean that the data can never be changed. In the case of a lawsuit, it can be difficult to prove that your intellectual property belongs to you and that you didn’t license anyone else to use it. With blockchain, all evidence is easily traceable as blockchain technology stores information about every entry. This makes it simple for an individual to obtain proof that their patent belongs to them. Also, smart contracts (digital programs that perform actions on their own) can be used for an owner to give licensed users access to the intellectual property. Blockchain’s ability for recording crypto transactions shows that it can be used in recording other valuable data securely and honestly.
In conclusion,
Blockchain is still a baby compared to other technologies and systems in place. It is still a mystery to many and might not seem like something that will catch on. However, this is only the beginning and soon, blockchain will have greater applications and be a part of our daily lives. Who would have thought that an anonymous publication in 2008 would have resulted in the next big thing since the Internet?